Solar System Comparisons
A solar system is comprised of 3 primary components , namely – photovoltaic solar panels (PV) , inverter and utility. Batteries and or Generators provide an additional element of energy supply for nighttime or utility power cuts.
The ideal system for your home or business depends on your infrastructure and desired results. Our consultants will design a system specifically tailored for your demand and desired outcome. The Solar Power System Comparisons below provide a basic overview of the differences between options.
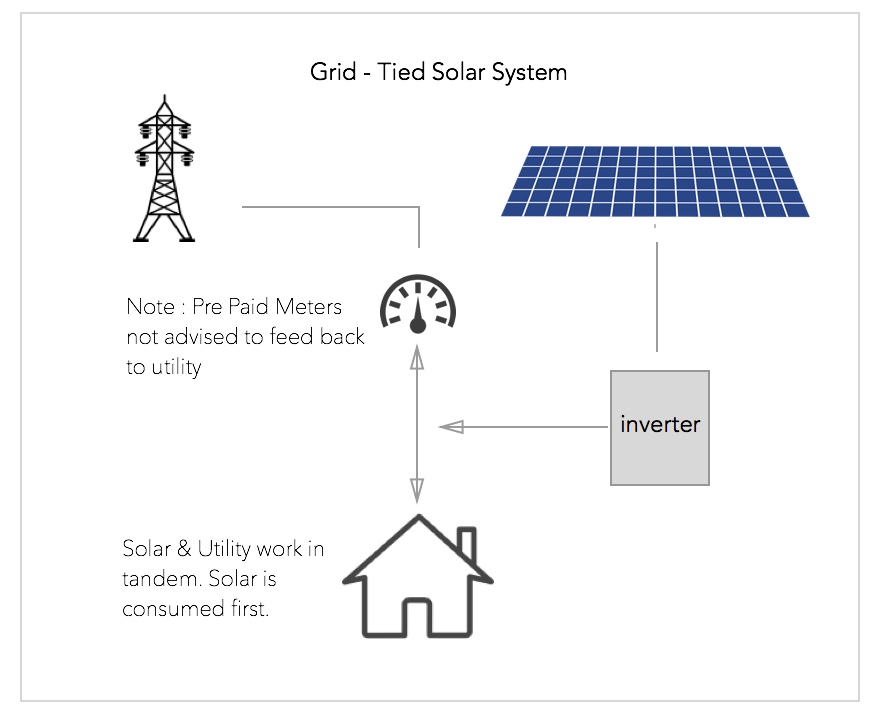
Option 1 Grid-Tied
A grid tied solar system is the most cost effective and efficient solar system.
- Not Impervious to Energy Black-outs
- Quickest Pay-Back Period
- Best ROI
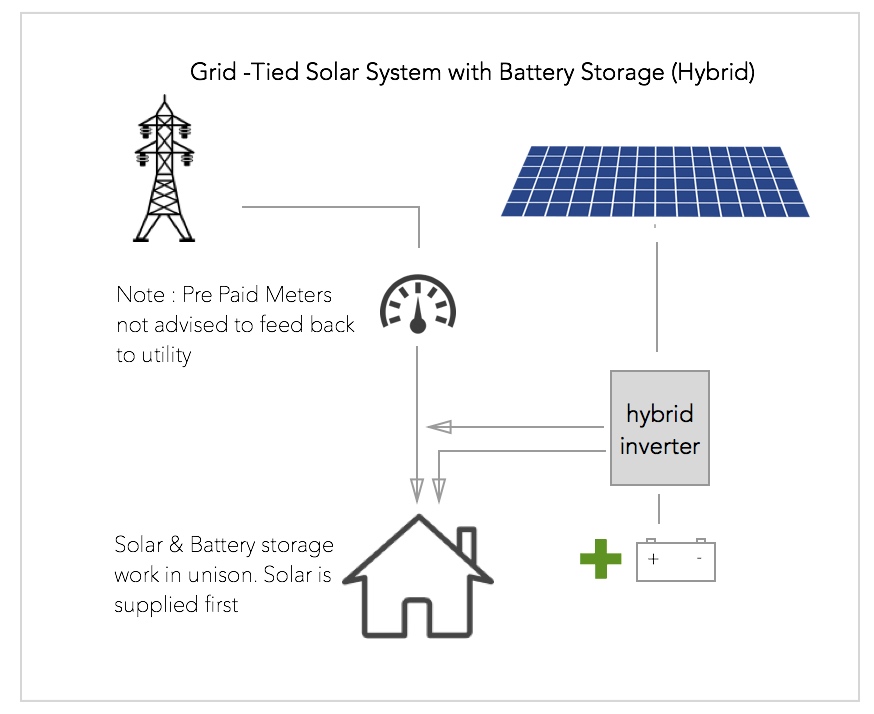
Option 2 – Grid-Tied with Storage (Hybrid)
A Hybrid inverter allows for the addition of battery and/or generator to supply load during power outages.
- More Expensive
- Impervious to Utility Outages
- Good ROI
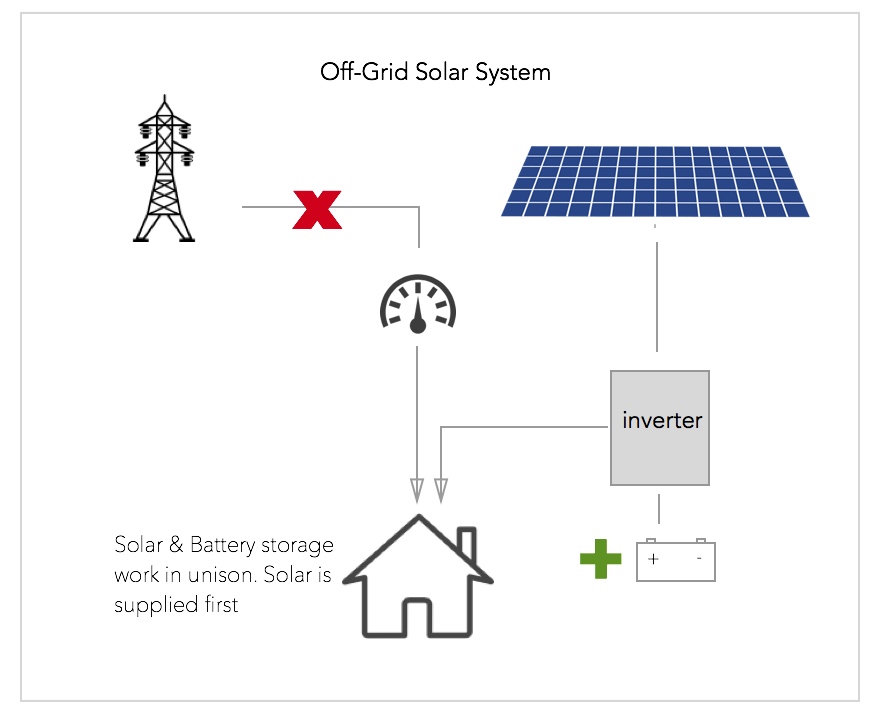
Option 3 – Off-Grid
An Off-Grid system supplies load via PV Solar and Batteries.
- Impervious to utility outages
- Piece of mind
- fair ROI
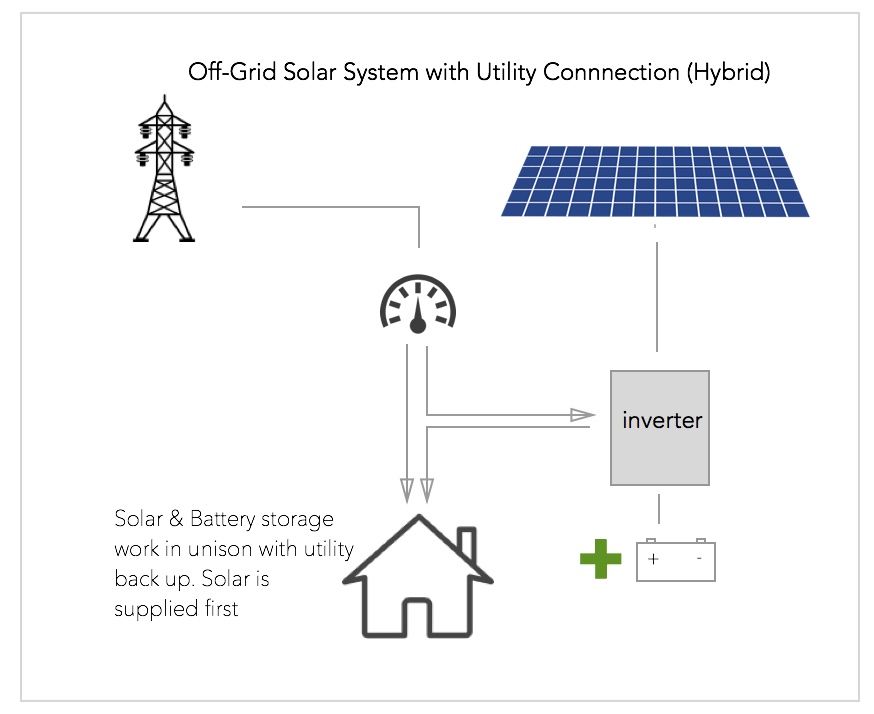
Option 4 – Off-Grid with Utility backup (Hybrid)
This option is the same as an Off-Grid system (above) with the added benefit of having utility supply as back up.
- More Expensive System
- Impervious to Utility Outages
- Greatest piece of mind
- Fair ROI
System Sizing
SolarXgen performs “load demand” reports, using energy monitoring devices. We are able to ascertain your home’s or businesses exact “time of use” consumption. Our proprietary software enables us to design the optimum system for your needs and quote accordingly.
A vast array of factors affect sizing and ultimate electricity production reports , including , but not limited to , site Azimuth, PV array inclination, spacing, mounting structures, site irradiation levels, module and inverter efficiency, dc wiring, ac wiring.






